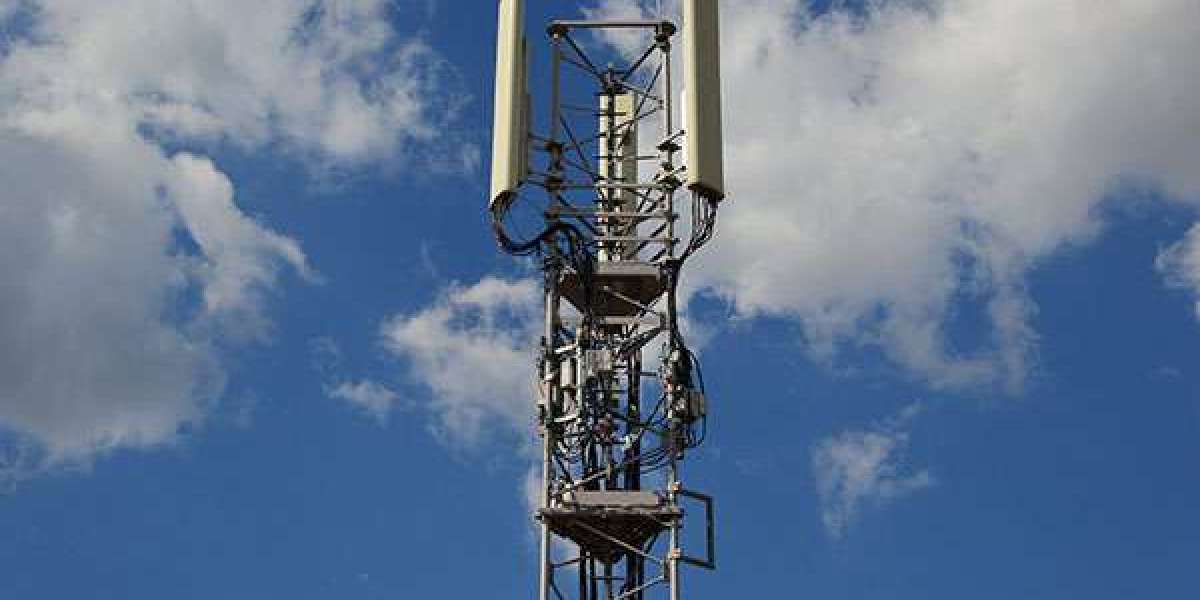
Telecommunications equipment is at the heart of modern communication networks, supporting everything from mobile phone services to broadband internet and cloud computing. These systems are crucial for daily operations in businesses, governments, and homes. To ensure that telecom infrastructure remains functional, reliable, and secure, Telecom Equipment Protection is essential.
Telecom equipment is often subjected to various environmental factors, physical threats, and operational challenges that can lead to damage, malfunction, or failure. Whether it's equipment housed in outdoor cabinets, data centers, or base stations, protecting telecom equipment is critical to maintaining service quality and minimizing downtime. This article delves into the different aspects of telecom equipment protection, including environmental considerations, physical security measures, and the technology used to safeguard telecom assets.
Key Threats to Telecom Equipment
Environmental Factors: Telecom equipment is exposed to environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, moisture, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Without proper protection, these conditions can cause corrosion, overheating, or electrical failure.
Vandalism and Theft: Telecom equipment is often located in public areas or remote locations, making it vulnerable to theft, vandalism, or sabotage. Unprotected or poorly secured equipment can be tampered with or stolen, leading to service outages or significant replacement costs.
Physical Impact: Equipment may face physical damage due to impacts from storms, animals, accidents, or accidental human error. Physical damage can range from minor dents and scratches to complete destruction of essential components.
Power Surges and Electrical Damage: Power surges caused by lightning strikes, faulty power supplies, or grid instability can damage sensitive electronic components of telecom equipment. These events can lead to system failures or even permanent equipment loss.
Cybersecurity Threats: While not directly related to physical damage, cybersecurity threats can compromise telecom systems by exposing them to hacking, data breaches, or denial-of-service attacks. These threats can undermine the functionality of telecom equipment and cause service disruptions.
Strategies for Telecom Equipment Protection
Weatherproof Enclosures
- One of the most effective ways to protect telecom equipment from environmental factors is through weatherproof enclosures. These enclosures shield equipment from rain, snow, dust, and extreme temperatures, ensuring that the equipment operates smoothly in all weather conditions. Enclosures with IP-rated protection (Ingress Protection) ensure that the cabinets or boxes are resistant to water and dust infiltration, providing a robust solution for outdoor installations.
- Common types of weatherproof enclosures include IP65, IP66, and IP67-rated cabinets which offer varying degrees of protection against dust and water ingress. These enclosures often come with ventilation and airflow management solutions to prevent overheating.
Rack-Mounted and Sealed Cabinets
- Rack-mounted cabinets or sealed enclosures are used to house telecom equipment safely, providing both security and environmental protection. These cabinets often feature locking doors, temperature regulation, and ventilation systems to protect against heat, moisture, and unauthorized access.
- Cooling solutions such as fans, air conditioning, or liquid cooling systems are integrated into these cabinets to maintain an optimal temperature inside, preventing overheating that could damage equipment.
Surge Protection
- Surge protection devices (SPDs) are essential to protect telecom equipment from power surges, lightning strikes, and voltage spikes. SPDs are installed between the power supply and the telecom equipment to divert excess voltage away from sensitive components.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are often used alongside surge protectors to provide backup power during outages and to protect equipment from sudden power failures. UPS units allow telecom systems to continue running temporarily while the main power source is restored or equipment is shut down safely.
Physical Security and Anti-Tampering Measures
- Physical security measures are critical to prevent theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access to telecom equipment. Common protection methods include:
- Lockable Cabinets and Doors: Cabinets are often fitted with locks to prevent unauthorized individuals from tampering with or stealing equipment.
- Fencing and Barriers: Perimeter fencing, gates, and barriers help deter unauthorized entry into telecom facilities or outdoor equipment enclosures.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: CCTV cameras, motion sensors, and intrusion detection systems can monitor and alert personnel to any unauthorized access attempts, helping prevent vandalism and theft.
- Tamper-Evident Seals: These seals indicate if someone has tampered with the equipment, alerting security personnel to any unauthorized activities.
- Remote Monitoring: Integrated monitoring systems allow operators to track the condition of telecom equipment and detect unauthorized access in real time.
- Physical security measures are critical to prevent theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access to telecom equipment. Common protection methods include:
Fire Protection Systems
- Fire suppression systems are essential in protecting telecom equipment from the risk of fire, particularly in enclosed spaces such as data centers, server rooms, or telecom cabinets. These systems are designed to quickly detect and extinguish fires before they can cause significant damage.
- Common fire protection solutions include sprinkler systems, clean agent fire suppression, and fire extinguishers tailored for use with electronic equipment.
Corrosion Prevention
- Telecom equipment located in humid or coastal areas is at a high risk of corrosion. Anti-corrosion coatings and materials are used to protect the internal and external components of telecom enclosures. Stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized steel are commonly used for enclosures exposed to harsh environments due to their resistance to rust and corrosion.
Electromagnetic Shielding
- Telecom equipment may be vulnerable to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt operations and lead to signal degradation or failure. To protect against EMI, enclosures are often equipped with electromagnetic shielding to minimize interference from external sources.
- Specialized EMI filters and shielded cables are also used to prevent interference in sensitive telecom systems.
Cybersecurity Protections
- While physical protection is essential, telecom systems must also be safeguarded from cybersecurity threats. This involves securing network connections, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring data privacy. Some best practices for securing telecom equipment include:
- Firewalls: To block unauthorized access to network infrastructure.
- Encryption: To protect sensitive data and communication.
- Access Control: Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to critical equipment and systems.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping equipment firmware and software up to date to prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): To monitor and detect any unusual network activity that may indicate a cyberattack.
- While physical protection is essential, telecom systems must also be safeguarded from cybersecurity threats. This involves securing network connections, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring data privacy. Some best practices for securing telecom equipment include:
Benefits of Telecom Equipment Protection
Improved Reliability: With proper protection, telecom equipment can operate reliably even in harsh environments. This ensures consistent service quality for customers and reduces the risk of unexpected downtime.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: Protecting equipment from environmental damage and wear reduces the need for repairs or replacements. This can lower maintenance costs and improve the overall cost-effectiveness of telecom operations.
Extended Lifespan: Protection methods such as surge protection, fire suppression, and corrosion prevention extend the life of telecom equipment, allowing operators to maximize their investments over time.
Enhanced Security: Effective physical and cybersecurity measures ensure that equipment remains secure, reducing the risk of theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access.
Compliance with Industry Standards: Telecom operators must adhere to industry regulations and standards regarding equipment safety, reliability, and performance. Proper equipment protection helps ensure compliance with these requirements.
Conclusion
Telecom equipment protection is essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure from environmental, physical, and cybersecurity threats. By implementing a combination of weatherproof enclosures, cooling solutions, surge protection, security measures, and fire suppression systems, telecom operators can ensure that their equipment remains operational and secure. As the reliance on telecommunications infrastructure continues to grow, protecting this equipment is paramount to delivering reliable, high-quality services and avoiding costly downtime.